Introduction to the German Shepherd Breed
The German Shepherd, known for its intelligence and versatility, originated in Germany in the late 19th century. Developed by Max von Stephanitz, this breed was designed for herding sheep and excelling in demanding tasks.
Over time, its adaptability made it a favorite in military, police, and search-and-rescue operations worldwide. German Shepherds are medium to large dogs, with a striking double coat, erect ears, and a confident, noble demeanor. Their loyalty, courage, and trainability stem from generations of selective breeding for working capabilities.
Renowned for their presence in popular media, German Shepherds like Rin Tin Tin and Strongheart have graced Hollywood screens, further cementing their reputation as iconic companions.
This breed’s work ethic and eagerness to please make them exceptional family pets, guardians, and working dogs. However, their robust nature requires proper care and understanding to ensure a healthy and fulfilling life.
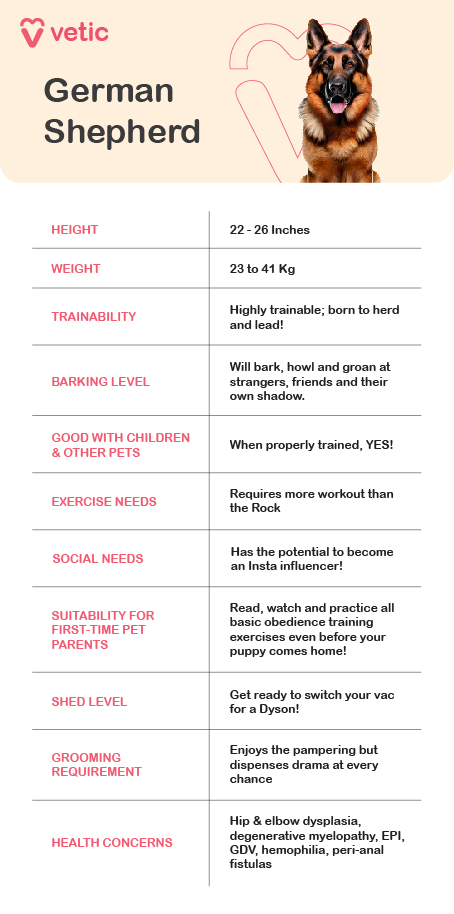
Common Health Concerns in German Shepherds
German Shepherds are prone to several genetic and breed-specific health issues, including:
- Hip and Elbow Dysplasia: Hip and elbow dysplasia includes abnormal joint development that causes pain, arthritis, and mobility issues.
- Degenerative Myelopathy: Progressive spinal cord disease leads to weakness and paralysis, often due to genetic predisposition.
- Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI): Lack of digestive enzymes results in weight loss and malabsorption of nutrients.
- Bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus): Rapid stomach swelling can twist that can become life-threatening without immediate intervention.
- Panosteitis (Growing Pains): Inflammation in young dogs’ long bones causes temporary lameness.
- Hemophilia: Genetic blood clotting disorder, mostly affecting male German Shepherds.
- Perianal Fistulas: Painful lesions around the anus, likely linked to immune and genetic factors.
To Reduce Health Risks, Pet Parents of German Shepherd Pups and Dogs Should –
- Consult a veterinarian immediately before or after bringing your puppy home.
- Maintain a healthy diet and weight for their breed, age and gender.
- Provide regular exercise appropriate to the dog’s age and health status.
- Schedule regular vet check-ups for early detection of potential health issues.
- Consider pet insurance to help manage potential healthcare costs.
German Shepherd Puppies: Complete Healthcare Guide
Nutrition and Feeding Guide for German Shepherd Puppies

Nutritional Needs:
German Shepherd (GSD) puppies have unique dietary requirements to support their rapid growth and development. A balanced diet with the right mix of protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals is crucial.
- Protein: High-quality animal protein is essential for muscle development. Look for foods that list chicken, lamb, turkey, or fish as the primary ingredient.
- Fats: Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, support brain development, healthy skin, and a shiny coat. Sources like fish oil and flaxseed are beneficial.
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice, oats, and sweet potatoes, provide steady energy levels for active puppies.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: These minerals are vital for bone and teeth development. The calcium-to-phosphorus ratio must be balanced to prevent skeletal issues.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential vitamins like A, D, and E, along with minerals such as zinc and selenium, support immune function and overall health.
Food Options:
- Commercial Puppy Food: Choose high-quality puppy food formulated for large breeds to ensure proper growth and joint health. Brands like Royal Canin offer tailored options for German Shepherd puppies.
- Homemade Diets: If opting for homemade meals, consult with a veterinarian to ensure a balanced diet. Include lean meats, vegetables, and whole grains.
Feeding Frequency and Timing:
- 8 Weeks to 6 Months: Feed 3-4 small meals per day to provide consistent energy and nutrients for growth.
- 6 Months and Older: Transition to 2 meals per day as the puppy’s growth rate slows down.
Stick to a regular feeding schedule to help with digestion and prevent overeating, which can lead to weight gain.
Grooming Essentials for German Shepherd Puppies
Coat Care:
German Shepherd puppies have a double coat that needs regular grooming to keep it healthy and free from tangles.
Brushing: Brush your German Shepherd puppy 2-3 times a week with a slicker brush to remove loose fur and help reduce shedding.
Shedding: Be prepared for increased shedding, particularly during the seasonal changes in spring and fall. During these times, brushing more often will help manage the shedding.
Bathing: Bathe your puppy every 2-3 months or when necessary, using a puppy-friendly shampoo that helps maintain their natural coat oils.
Ear Cleaning: Clean your puppy’s ears once a week to prevent infections. Use a vet-approved ear cleaner and cotton balls for a gentle cleanse.
Nail Trimming: Trim your puppy’s nails every 3-4 weeks to avoid overgrowth and any discomfort.
Dental Care:
Brush your German Shepherd puppy’s teeth 2-3 times a week using dog-specific toothpaste and brush to ensure good oral health and prevent tartar buildup.
Preventive Care and Vaccination Schedule for German Shepherd Pups
Vaccinations:
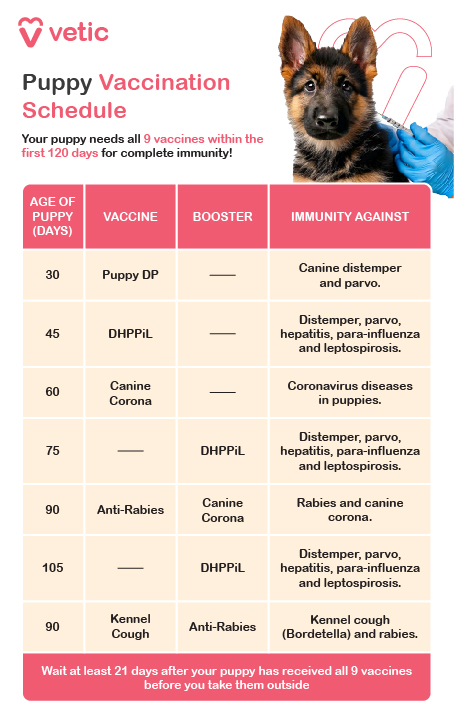
German Shepherd puppies require a series of vaccinations to protect them from common canine diseases. Follow your veterinarian’s recommended vaccination schedule.
- 6-8 Weeks: First vaccination for distemper, parvovirus, and hepatitis.
- 10-12 Weeks: Second round of vaccinations for distemper, parvovirus, and hepatitis; first Bordetella (kennel cough) vaccine.
- 14-16 Weeks: Third round of vaccinations, including rabies, leptospirosis, and parainfluenza.
- 6-12 Months: Booster shots for rabies and other core vaccines as recommended by your vet.
Parasite Control:

- Flea and Tick Prevention: Start flea and tick prevention treatments at 8 weeks of age. Use products safe for puppies.
- Heartworm Prevention: Begin heartworm prevention around 8-12 weeks of age, as recommended by your veterinarian.
- Deworming: Puppies should be dewormed regularly, starting at 2-3 weeks of age and continuing every few weeks until 12 weeks. Consult your vet for a specific deworming schedule.
Regular Vet Check-ups:
Schedule regular veterinary visits for wellness checks, vaccination updates, and monitoring your puppy’s growth and development.
Health Risks and What to Watch Out For in GSD Puppies
Common Health Risks:
German Shepherds are prone to certain genetic and developmental health issues. Early detection and preventive care are essential.
- Hip Dysplasia: Monitor for signs of discomfort, limping, or difficulty rising, especially after exercise. Maintain a healthy weight and avoid excessive jumping or running on hard surfaces.
- Elbow Dysplasia: Similar to hip dysplasia, this condition affects the elbow joints. Watch for front leg lameness or swelling.
- Panosteitis: Panosteitis affects growing bones, causing lameness in young German Shepherds. It usually resolves as the puppy matures.
- Bloat (Gastric Torsion): Although more common in adults, puppies can still be at risk. Avoid large meals and vigorous exercise immediately after eating.
Signs to Watch For:
- Unusual lethargy or reluctance to play
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhoea
- Difficulty breathing or persistent coughing
- Excessive scratching, licking, or biting at the skin
- Limping or signs of pain when moving
Contact your veterinarian immediately if any of these symptoms are observed.
Activities, Exercise, and Training for GSD Puppies
Physical Activities:
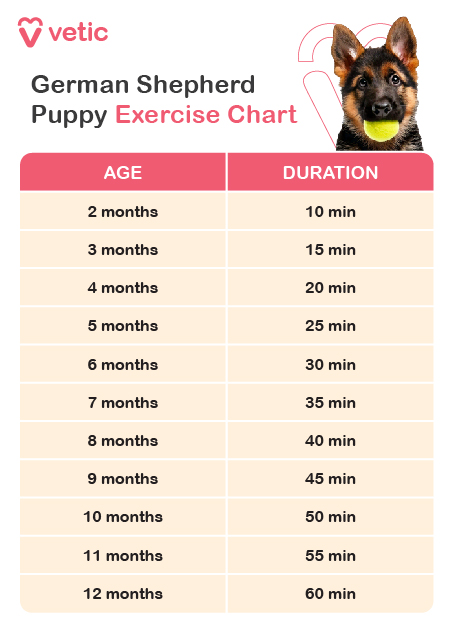
German Shepherd puppies are energetic and need regular exercise to develop strong muscles and prevent boredom. However, care must be taken to avoid over-exercising, which can harm developing joints.
- Short Walks: Begin with short walks, gradually increasing the duration as your puppy grows. Aim for 15-20 minutes, twice a day.
- Playtime: Engage in interactive play sessions, such as fetch, or playing with other dogs, to stimulate their mind and body.
- Socialization: Introduce your puppy to various environments, people, and other animals to help them develop confidence and good social skills.
Training:
German Shepherd puppies are intelligent and respond well to training. Early training establishes good behavior and obedience.
- Basic Commands: Teach commands like “sit,” “stay,” “come,” and “down” using positive reinforcement with treats, praise, and play.
- Crate Training: Crate training provides a safe space for your puppy and helps with housebreaking. Make the crate a positive environment with treats and toys.
- Leash Training: Start leash training early to encourage good walking habits and reduce pulling.
Mental Stimulation:
Provide puzzle toys, interactive toys, and obedience training to keep your puppy mentally engaged and prevent boredom.
Behavior Problems and Solutions in GSD Puppies
Common Behavior Issues: German Shepherd puppies are intelligent and eager to learn, but without proper guidance, they can develop some behavioral problems.
- Chewing: Puppies explore the world with their mouths. Provide plenty of chew toys to prevent destructive chewing. Puppy-proof your home by removing items that could be chewed or swallowed.
- Biting: Puppy biting is normal. Redirect biting to appropriate toys and use positive reinforcement to discourage biting people.
- Jumping Up: German Shepherds are friendly and may jump up to greet people. Teach the “sit” command to discourage jumping and reward calm behavior.
- Separation Anxiety: These puppies can become anxious when left alone. Gradually increase the time your puppy spends alone, providing toys and treats to keep them occupied.
Behavioral Training Solutions:
- Positive Reinforcement: Use treats, praise, and play to reward good behavior. Avoid harsh punishment, as it can lead to fear and anxiety.
- Consistency: Be consistent with commands and routines to help your puppy understand expectations.
- Socialization: Expose your puppy to various environments, people, and other dogs to develop good social skills and prevent fear or aggression.
Managing Excess Energy:
German Shepherd puppies have high energy levels. Ensure they receive enough physical and mental stimulation daily to prevent boredom and destructive behavior. Regular exercise, training sessions, and playtime are key to keeping your puppy happy and well-behaved.
Adolescent or Young Adult German Shepherd Puppies: Complete Healthcare Guide
Nutrition for Adolescent German Shepherds

Nutritional Needs:
During adolescence, German Shepherds continue to grow and develop muscle mass, requiring a diet that supports their increased energy needs and ongoing growth.
- Protein: High-quality animal protein is essential for muscle development and overall health. Look for dog food with real meat sources like chicken, lamb, or fish as the main ingredient.
- Fats: Healthy fats provide energy and support skin and coat health. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from sources like fish oil are beneficial.
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, oats, and sweet potatoes provide sustained energy for active adolescents.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: These minerals support bone growth and density. Ensure a balanced ratio to prevent skeletal issues common in large breeds.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins A, D, E, and B-complex, along with minerals like zinc and selenium, boost immune function and overall health.
Food Options:
- Commercial Dog Food: Choose high-quality dog food formulated for large breeds that cater to their specific growth and energy needs. Brands like Royal Canin, and Orijen offer suitable options for adolescent German Shepherds.
- Homemade Diets: If you prefer homemade meals, consult with a veterinarian to ensure the diet meets all nutritional requirements. Include lean meats, vegetables, and whole grains.
Feeding Frequency and Timing:
- Feeding Schedule: Feed your adolescent German Shepherd 2-3 times per day to provide consistent energy. This helps prevent overeating and reduces the risk of bloat (gastric torsion).
- Portion Control: Monitor portion sizes to maintain a healthy weight, adjusting based on activity level and growth.
Grooming Necessities and Frequency for Young Adult GSD Puppies

Coat Care:
German Shepherds have a double coat that requires regular grooming to keep it healthy and free of mats.
- Brushing: Brush your adolescent German Shepherd’s coat 2-3 times a week with a slicker brush or undercoat rake to remove loose hair and reduce shedding.
- Shedding: Expect increased shedding, especially during seasonal changes (spring and fall). More frequent brushing is needed during these times.
- Bathing: Bathe your German Shepherd every 2-3 months or as needed, using a dog-specific shampoo that maintains their coat’s natural oils.
- Ear Cleaning: Clean your dog’s ears weekly to prevent infections. Use a vet-recommended ear cleaner and cotton balls.
- Nail Trimming: Trim your dog’s nails every 3-4 weeks to prevent overgrowth and discomfort.
Dental Care:
Brush your German Shepherd’s teeth 2-3 times per week using dog-specific toothpaste to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent tartar buildup.
Preventive Care and Vaccination Schedule for GSD Adolescents

Vaccinations:
Ensure your German Shepherd stays up-to-date on vaccinations to protect against common canine diseases.
- Core Vaccines: Rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus vaccines are essential. Follow your vet’s recommended schedule for boosters.
- Optional Vaccines: Depending on lifestyle, consider vaccinations for Bordetella (kennel cough) and canine coronavirus.
Parasite Control:
- Flea and Tick Prevention: Use timely flea and tick prevention treatments, especially if your dog spends time outdoors.
- Heartworm Prevention: Administer monthly heartworm preventives. Heartworm disease can be serious, so consistent prevention is crucial.
- Regular Deworming: Deworming every 3-6 months is recommended, especially if your German Shepherd frequently plays outdoors or with other dogs.
Regular Vet Check-ups:
Schedule regular veterinary visits for health check-ups, vaccination updates, and monitoring your German Shepherd’s growth and development.
Health Risks and What to Watch Out For in Adolescent GSD Pups
Common Health Risks:
Adolescent German Shepherds are still at risk for some genetic and developmental health issues. Early detection and preventive care are key.
- Hip Dysplasia: This genetic condition can cause pain and mobility issues. Maintain a healthy weight and provide moderate exercise to prevent joint strain.
- Elbow Dysplasia: Monitor for front leg lameness or swelling. Regular check-ups with your vet can help detect and manage joint problems.
- Panosteitis (Growing Pains): This condition can cause intermittent lameness in young dogs. Symptoms usually resolve with age.
- Bloat (Gastric Torsion): German Shepherds are prone to bloat. Feed smaller meals more frequently and avoid vigorous exercise immediately after eating.
Signs to Watch For:
- Reluctance to play or exercise
- Limping or difficulty rising after resting
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhoea
- Excessive scratching or skin irritation
Contact your veterinarian immediately if you notice any of these symptoms.
Activities, Exercise, and Training for Young Adult GSD
Physical Activities:
German Shepherd adolescents are full of energy and require regular exercise to develop strong muscles, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent behavioural issues.
- Daily Walks: Aim for 1-2 long walks per day, totaling about 60-90 minutes. Walks should be brisk to allow your German Shepherd to expend energy.
- Playtime: Engage in interactive games such as fetch, frisbee, or sniff-and-seek the treats. These activities provide physical exercise and mental stimulation.
- Agility Training: Start introducing basic agility training to keep them mentally challenged and physically fit. This also helps with coordination and obedience.
- Swimming: If accessible, swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise that builds strength and stamina without putting too much stress on developing joints.
Training:
Training should continue throughout adolescence, focusing on obedience, socialisation, and addressing any behavioural issues.
- Obedience Training: Reinforce basic commands like “sit,” “stay,” “come,” “heel,” and “down.” Use positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise.
- Advanced Commands: Introduce more complex commands and tricks. Training sessions should be engaging and consistent to keep their interest.
- Leash Training: Continue leash training to prevent pulling and encourage good walking manners.
- Socialisation: Continue to expose your German Shepherd to various people, animals, and environments to build confidence and reduce anxiety.
Mental Stimulation:
Provide puzzle toys, interactive games, and training exercises that challenge their problem-solving abilities. This helps keep them mentally sharp and prevents boredom.
Behaviour Problems and Solutions for Junior GSD Pups

Common Behaviour Issues:
German Shepherd adolescents are intelligent and energetic but can develop behaviour problems if not properly trained and exercised.
- Chewing: Chewing is common during teething and boredom. Provide chew toys and keep valuables out of reach. Regular exercise can also reduce destructive chewing.
- Jumping Up: German Shepherds may jump on people out of excitement. Teach the “sit” command and reward calm behaviour. Consistent training is key to discouraging jumping.
- Biting/Nipping: Adolescents may nip due to teething or playfulness. Redirect biting to appropriate toys and reinforce gentle play.
- Separation Anxiety: Adolescents can develop anxiety when left alone. Gradually increase alone time, providing toys and treats to keep them occupied.
Behavioral Training Solutions:
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward good behaviour with treats, praise, and playtime. Avoid harsh punishment, as it can lead to fear and anxiety.
- Consistency: Be consistent with commands, routines, and training sessions. This helps your German Shepherd understand expectations.
- Socialisation: Continue to expose your adolescent dog to various environments, people, and other dogs to develop social skills and prevent fear or aggression.
Managing Excess Energy:
Regular physical and mental exercise is crucial to prevent boredom and frustration. Daily walks, playtime, training, and interactive toys help keep your German Shepherd mentally stimulated and well-behaved.
Adult German Shepherd: Complete Healthcare Guide

Nutrition for Adult German Shepherds
Nutritional Needs:
Adult German Shepherds require a food that supports their active lifestyle, maintains their muscle mass, and promotes overall health.
- Protein: High-quality animal protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and overall health. Look for dog foods that list real meat, such as chicken, beef, lamb, or fish, as the primary ingredient.
- Fats: Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, support skin and coat health, joint function, and overall vitality. Fish oil and flaxseed are excellent sources.
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice, oats, and sweet potatoes, provide sustained energy, which is essential for an active breed like the German Shepherd.
- Fibre: A moderate amount of fibre aids digestion and prevents gastrointestinal issues. Ingredients like beet pulp and pumpkin are good sources of dietary fibre.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins A, D, E, and B-complex, along with essential minerals like zinc and selenium, support immune function, skin health, and overall well-being.
Food Options:
- Commercial Dog Food: Opt for high-quality dog food specifically formulated for large breeds, focusing on balanced nutrition. Brands like Royal Canin, and Orijen offer options tailored to the needs of adult German Shepherds.
- Homemade Diets: If preparing homemade meals, ensure they are nutritionally balanced. Include a variety of lean meats, vegetables, and whole grains. Consulting a veterinarian or canine nutritionist is recommended.
Feeding Frequency and Timing:
- Feeding Schedule: Feed your adult German Shepherd twice a day—morning and evening. This helps maintain a stable energy level throughout the day.
- Portion Control: Monitor portion sizes to avoid overfeeding, which can lead to obesity. Adjust the amount based on your dog’s activity level, metabolism, and overall health.
Grooming Necessities and Frequency for Adult GSDs

Coat Care:
German Shepherds have a dense double coat that requires regular grooming to keep it healthy and minimise shedding.
- Brushing: Brush your German Shepherd’s coat 2-3 times a week with a slicker brush or undercoat rake to remove loose hair and reduce shedding.
- Shedding: Be prepared for increased shedding during the seasonal shedding periods (spring and fall). During these times, daily brushing may be necessary.
- Bathing: Bathe your German Shepherd every 1-1.5 months or as needed, using a dog-specific shampoo that maintains the coat’s natural oils.
- Ear Cleaning: Clean your dog’s ears weekly to prevent infections. Use a vet-recommended ear cleaner and cotton balls to gently clean the ear canal.
- Nail Trimming: Trim your dog’s nails every 3-4 weeks to prevent overgrowth and discomfort. Regular trimming is essential to maintain healthy feet.
Dental Care:
Brush your dog’s teeth 2-3 times a week using dog-specific toothpaste to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent dental issues such as tartar buildup and gum disease.
Preventive Care and Health Monitoring of Adult GSDs
Regular Vet Check-ups:
Schedule regular veterinary visits at least once a year for wellness checks, vaccination updates, and monitoring your German Shepherd’s overall health. These visits help detect potential health issues early.
Vaccinations:
Ensure your dog stays up-to-date on all core vaccinations, including rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus. Depending on your dog’s lifestyle, additional vaccines for Bordetella (kennel cough), Canine corona, or leptospirosis may be recommended.
Parasite Control:

- Flea and Tick Prevention: Administer monthly flea and tick preventives to protect your dog from parasites, especially if they spend a lot of time outdoors.
- Heartworm Prevention: Continue administering monthly heartworm prevention medication. Heartworm disease is serious and can be fatal, so consistent prevention is crucial.
- Deworming: Regular deworming every 3-6 months is advised, particularly if your German Shepherd spends time in areas where they may be exposed to parasites.
Health Risks and What to Watch For:
German Shepherds are prone to certain genetic and breed-specific health issues. Regular monitoring and preventive care are essential to keeping them healthy.
- Hip and Elbow Dysplasia: These genetic conditions can cause pain and mobility issues. Maintain a healthy weight and provide joint supplements if recommended by your vet.
- Degenerative Myelopathy: This is a progressive spinal cord disease that can affect older German Shepherds. Watch for signs of hind leg weakness or difficulty walking.
- Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus (Bloat): German Shepherds are at risk of bloat, a life-threatening condition. To reduce the risk, feed smaller, more frequent meals and avoid vigorous exercise immediately after eating.
- Pancreatic Insufficiency: Monitor for signs of digestive issues such as weight loss despite a good appetite, chronic diarrhoea, or vomiting.
Signs to Watch For:
- Sudden changes in appetite or weight
- Limping, leg stiffness, or difficulty rising
- Unexplained lethargy or lack of interest in activities
- Persistent coughing or difficulty breathing
- Vomiting or diarrhoea that lasts more than 24 hours
Contact your veterinarian immediately if you notice any concerning symptoms.
Activities, Exercise, and Training for an Adult GSD

Physical Activities:
German Shepherds are active and energetic dogs that require regular exercise to stay healthy, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent behavioural issues.
- Daily Exercise: Provide at least 60-90 minutes of exercise daily. This can include brisk walks, jogging, hiking, or playing fetch. Regular exercise helps prevent obesity and keeps their joints healthy.
- Playtime: Engage in interactive games like fetch, frisbee, or tug-of-war. These activities not only provide physical exercise but also strengthen the bond between you and your dog.
- Agility Training: Adult German Shepherds excel in agility training, which provides both physical and mental stimulation. Set up an agility course in your backyard or participate in organised agility classes.
- Swimming: Swimming is a low-impact exercise that’s easy on the joints and an excellent way to burn off energy.
Training:
Training remains essential throughout adulthood to reinforce good behaviour and obedience.
- Obedience Training: Continue reinforcing basic commands like “sit,” “stay,” “come,” and “heel.” Regular training sessions help maintain their discipline and responsiveness.
- Advanced Training: Consider advanced obedience training, trick training, or specialised training like scent work. German Shepherds are highly trainable and enjoy challenges.
- Leash Training: Ensure your dog remains well-behaved on the leash, particularly during walks. This prevents pulling and makes walks more enjoyable for both of you.
Mental Stimulation:
Provide puzzle toys, interactive games, and training exercises that challenge their problem-solving abilities. Mental stimulation is just as important as physical exercise for this intelligent breed.
Behaviour Problems and Solutions of an Adult GSD

Common Behaviour Issues:
Even well-trained adult German Shepherds can exhibit certain behaviour problems, often due to boredom, lack of exercise, or insufficient mental stimulation.
- Barking: German Shepherds can be vocal, often barking at strangers, other animals, or even out of boredom. Training your dog to follow the “quiet” command and ensuring they get enough exercise can help manage excessive barking.
- Chewing: Destructive chewing can occur if your dog is bored or anxious. Provide plenty of chew toys and keep them mentally and physically stimulated.
- Separation Anxiety: German Shepherds form strong bonds with their owners and can become anxious when left alone. Gradually increase alone time and provide toys or treats to keep them occupied.
- Aggression: German Shepherds are protective by nature. Proper socialisation from an early age and consistent training can prevent aggressive behaviours towards strangers or other animals.
Behavioral Training Solutions:
- Positive Reinforcement: Continue using positive reinforcement techniques such as treats, praise, and playtime to reward good behaviour.
- Consistency: Be consistent with commands, routines, and training sessions. This helps your German Shepherd understand expectations and reduces the likelihood of behaviour issues.
- Socialisation: Ongoing socialisation is important to ensure your German Shepherd remains well-behaved around people, other dogs, and in different environments.
Managing Excess Energy:
Regular physical and mental exercise is key to preventing boredom and frustration. Daily walks, playtime, and training sessions help keep your German Shepherd mentally stimulated and well-behaved.
Complete Healthcare Guide for Senior German Shepherds
Nutrition for Senior German Shepherds

Nutritional Needs:
Senior German Shepherds require a diet that supports joint health, manages weight, and provides adequate nutrition without excess calories.
- Protein: High-quality animal protein is still essential for muscle maintenance. Opt for easily digestible protein sources like chicken, turkey, or fish.
- Fats: Healthy fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, support joint health, cognitive function, and a healthy coat. Look for foods enriched with fish oil or flaxseed oil.
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates like brown rice and oats provide energy without causing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. These are easier to digest and help manage energy levels.
- Fibre: Increased dietary fibre aids digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. Ingredients like beet pulp, sweet potatoes, and pumpkin are good fibre sources.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins C and E, along with antioxidants, support immune health. Glucosamine and chondroitin are beneficial for joint support, helping to alleviate symptoms of arthritis or joint stiffness common in older dogs.
Food Options:
- Commercial Senior Dog Food: Look for high-quality senior dog food formulated specifically for older dogs of large breeds. Brands like Royal Canin, Orijen and Acana offer senior formulas with adjusted calories and nutrients to suit the needs of older German Shepherds.
- Homemade Diets: If preparing homemade meals, ensure they are balanced and include lean meats, vegetables, and whole grains. Consulting with a veterinarian or a canine nutritionist can help tailor the diet to your senior dog’s needs.
Feeding Frequency and Timing:
- Feeding Schedule: Feed your senior German Shepherd two smaller meals a day—morning and evening. Smaller, more frequent meals can help with digestion and prevent issues like bloat.
- Portion Control: Monitor food intake carefully to prevent obesity, a common issue in senior dogs due to reduced activity levels.
Grooming Necessities and Frequency

Coat Care:
German Shepherds have a thick double coat that requires regular grooming even in their senior years to keep it healthy and minimise shedding.
- Brushing: Brush your senior German Shepherd’s coat 2-3 times a week using a slicker brush and undercoat rake. Regular brushing helps remove loose hair and reduces shedding.
- Shedding: Be prepared for increased shedding during seasonal changes. Daily brushing during these times can help manage the extra hair.
- Bathing: Bathe your German Shepherd every 2-3 months or as needed, using a shed reducing shampoo that reduces shedding and maintains the coat’s natural oils. Avoid over-bathing, as it can dry out their skin.
- Ear Cleaning: Clean your dog’s ears weekly to prevent infections. Use a vet-recommended ear cleaner and cotton balls to gently clean the ear canal.
- Nail Trimming: Trim your dog’s nails every 3-4 weeks. Regular trimming is essential to prevent discomfort and maintain healthy feet, especially as your dog’s activity level decreases.
Dental Care:
Dental hygiene is critical for senior dogs. Brush your German Shepherd’s teeth 2-3 times a week using dog-specific toothpaste to prevent dental issues, such as tartar buildup, gum disease, and tooth loss.
Preventive Care and Health Monitoring

Regular Vet Check-ups:
As your German Shepherd ages, regular veterinary visits become even more important. Schedule check-ups every 6 months to monitor your dog’s overall health, detect potential health issues early, and keep vaccinations up to date.
Vaccinations:
Ensure your dog remains up-to-date on core vaccinations, including rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus. Consult your vet to determine if additional vaccines are needed based on your dog’s lifestyle and health status.
Parasite Control:
- Flea and Tick Prevention: Continue monthly flea and tick preventives, especially if your dog spends time outdoors. These parasites can cause skin irritation and spread diseases.
- Heartworm Prevention: Administer monthly heartworm prevention medication, even in senior dogs. Heartworm disease is serious and can be fatal, so consistent prevention is crucial.
- Deworming: Regular deworming every 3-6 months is recommended, especially if your German Shepherd frequently interacts with other dogs or explores outdoor areas.
Health Risks and What to Watch For:
Senior German Shepherds are more prone to certain age-related health issues. Regular monitoring and preventive care are key to keeping them comfortable and healthy.
- Arthritis: Joint stiffness and pain are common in senior German Shepherds. Look for signs such as limping, difficulty rising, or reluctance to climb stairs. Supplements containing glucosamine and chondroitin, as well as anti-inflammatory medications, can help manage symptoms.
- Hip and Elbow Dysplasia: These genetic conditions can worsen with age. Monitor for changes in gait, mobility, or pain, and consult your vet for appropriate management options.
- Degenerative Myelopathy: This progressive spinal cord disease can lead to hind leg weakness and coordination loss. Early diagnosis and supportive care can help manage symptoms.
- Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome (CDS): Also known as canine dementia, CDS can cause confusion, disorientation, and changes in behaviour. Engage in mental stimulation and consult your vet for management options.
- Bloat (Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus): Older German Shepherds are still at risk of bloat. Feed smaller, more frequent meals and avoid vigorous exercise immediately after eating.
Signs to Watch For:
- Sudden weight loss or gain
- Changes in appetite or drinking habits
- Increased lethargy or reluctance to exercise
- Coughing, difficulty breathing, or persistent sneezing
- Vomiting, diarrhoea, or changes in bowel movements
Contact your veterinarian immediately if you notice any of these symptoms or other concerning changes in your dog’s health or behaviour.
Activities, Exercise, and Training

Physical Activities:
Although senior German Shepherds may not be as active as they once were, regular, gentle exercise is crucial for maintaining joint health, muscle tone, and mental stimulation.
- Daily Walks: Aim for 20-30 minutes of low-impact walks each day. Shorter, more frequent walks are ideal, allowing your dog to enjoy the outdoors without straining their joints.
- Gentle Play: Engage in gentle play sessions using toys gentle to their teeth. Avoid high-impact activities that can strain the joints.
- Swimming: Swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise that’s easy on the joints and helps build muscle without causing pain or discomfort. If possible, provide access to a safe swimming area.
- Stretching and Massage: Gentle stretching and massage can help improve flexibility and relieve joint stiffness. Regular massages can also help with blood circulation and relaxation.
Training:
Training remains important in the senior years to keep your German Shepherd mentally engaged and responsive.
- Obedience Refresher: Continue with basic obedience training. Use positive reinforcement, such as treats and praise, to keep training sessions enjoyable.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Introduce simple puzzle toys or treat-dispensing toys to stimulate your senior dog’s mind. These activities can help prevent cognitive decline.
- Leash Training: Ensure your dog remains well-behaved on the leash, especially during walks. This prevents pulling and reduces the risk of injury.
Mental Stimulation:
Mental engagement is important to prevent boredom and cognitive decline. Incorporate new activities, like scent games, that don’t require a lot of physical exertion but still keep their mind active.
Behaviour Problems and Solutions
Common Behaviour Issues:
Senior German Shepherds may exhibit behaviour changes due to ageing, discomfort, or cognitive decline. Understanding these changes and addressing them with patience is essential.
- Anxiety: Older dogs may become more anxious, especially when left alone. Provide a calm environment, and consider calming supplements or pheromone diffusers to help manage anxiety.
- Aggression: Pain or confusion due to cognitive decline can lead to irritability or aggression. Ensure regular vet check-ups to address any underlying health issues.
- House Soiling: Senior dogs may have accidents indoors due to decreased bladder control or cognitive issues. Regular bathroom breaks, especially after meals and before bedtime, can help manage this issue.
- Vocalization: Increased barking, whining, or howling can be a sign of pain, discomfort, or cognitive decline. Address any medical concerns and provide comfort and reassurance.
Behavioral Training Solutions:
- Positive Reinforcement: Continue using positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise, to encourage good behaviour and strengthen the bond between you and your senior dog.
- Routine: Maintain a consistent daily routine for feeding, exercise, and bathroom breaks. A predictable routine helps reduce anxiety and confusion.
- Comfort: Provide a comfortable bed and a quiet space for your senior German Shepherd to rest. Orthopaedic beds can help alleviate joint pain.
Managing Mental and Physical Changes:
Regular, gentle exercise and mental stimulation are important to keep your senior German Shepherd engaged and healthy. Adapt activities to suit their energy level and physical capabilities, and provide plenty of love and attention to support their emotional well-being.
Should You Adopt a German Shepherd?
Caring for a German Shepherd throughout their life requires dedication, attention, and a commitment to meeting their physical, mental, and emotional needs. From the playful, curious puppy phase to the mature, wise adult years, each stage comes with its own set of challenges and rewards.
Providing proper nutrition, regular exercise, mental stimulation, and preventive healthcare at each stage ensures that your German Shepherd remains healthy, happy, and well-behaved. By following a consistent care routine and maintaining close communication with your veterinarian, you can help your German Shepherd live a fulfilling, active life while strengthening the bond between you and your loyal companion.
